
Exclusive: Critical U.S. Election Systems Have Been Left Exposed Online Despite Official Denials
Exclusive: Critical U.S. Election Systems Have Been Left Exposed Online Despite Official Denials
The top voting machine company in the country insists that its election systems are never connected to the internet. But researchers found 35 of the systems have been connected to the internet for months and possibly years, including in some swing states.
For years, U.S. election officials and voting machine vendors have insisted that critical election systems are never connected to the internet and therefore can’t be hacked.
But a group of election security experts have found what they believe to be nearly three dozen backend election systems in 10 states connected to the internet over the last year, including some in critical swing states. These include systems in nine Wisconsin counties, in four Michigan counties, and in seven Florida counties—all states that are perennial battlegrounds in presidential elections.
Some of the systems have been online for a year and possibly longer. Some of them disappeared from the internet after the researchers notified an information-sharing group for election officials last year. But at least 19 of the systems, including one in Florida’s Miami-Dade County, were still connected to the internet this week, the researchers told Motherboard.
The researchers and Motherboard have been able to verify that at least some of the systems in Wisconsin, Rhode Island, and Florida are in fact election systems. The rest are still unconfirmed, but the fact that some of them appeared to quickly drop offline after the researchers reported them suggests their findings are on the mark.
“We … discovered that at least some jurisdictions were not aware that their systems were online,” said Kevin Skoglund, an independent security consultant who conducted the research with nine others, all of them long-time security professionals and academics with expertise in election security. Skoglund is also part of an advisory group, not associated with the research, that is working with the National Institute of Standards and Technology to develop new cybersecurity standards for voting machines. “In some cases, [the vendor was] in charge [of installing the systems] and there was no oversight. Election officials were publicly saying that their systems were never connected to the internet because they didn't know differently."
The systems the researchers found are made by Election Systems & Software, the top voting machine company in the country. They are used to receive encrypted vote totals transmitted via modem from ES&S voting machines on election night, in order to get rapid results that media use to call races, even though the results aren’t final.
Generally, votes are stored on memory cards inside the voting machines at polling places. After an election, poll workers remove these and drive them to county election offices. But some counties want to get their results faster, so they use wireless modems, either embedded in the voting machines or externally connected to them, to transmit the votes electronically. The system that receives these votes, called an SFTP server, is connected to the internet behind a Cisco firewall.
For security reasons, the SFTP server and firewall are only supposed to be connected to the internet for a couple of minutes before an election to test the transmission, and then for long enough after an election to transmit the votes. But the researchers found some of the systems connected to the internet for months at a time, and year-round for others, making them vulnerable to hackers.
Hacking the firewall and SFTP server would allow an attacker to potentially intercept the results as they’re transmitted and send fake results to the FTP server, depending on how securely the ES&S system authenticates the data. Although the election results that are transmitted via modem are unofficial—official votes are taken directly from the voting machine memory cards when they arrive at county offices—a significant discrepancy between the unofficial tallies and the official ones would create mistrust in the election results and confusion about which ones were accurate.
"These are all secure technologies that if [configured] correctly work just fine. It’s just that we have no faith that they are done correctly."
But Motherboard has learned that connected to the firewalls are even more critical backend systems—the election-reporting module that tabulates the unofficial votes as well as the official ones, and the election-management system that is used in some counties to program voting machines before elections. The researchers said that gaining access through the firewall to these systems could potentially allow a hacker to alter official election results or subvert the election-management system to distribute malware to voting machines through the USB flash drives that pass between this system and the voting machines.
*
Online, the researchers can only see the firewalls configured in front of these systems and cannot see anything behind them—a federal law makes it illegal for them to probe beyond the firewall. But ES&S documents posted online in various counties show that these critical backend systems are connected to the firewall, and ES&S also confirmed to Motherboard that this is the correct architecture in counties that want to transmit results electronically.
ES&S has long insisted that election-management systems are air-gapped—that is, not connected to the internet or connected to any other system that is connected to the internet—and the company insists to Motherboard that the diagram it provided isn’t showing them connected to the internet.
“There’s nothing connected to the firewall that is exposed to the internet,” Gary Weber, vice president of software development and engineering for ES&S, told Motherboard. “Our [election-management system] is not pingable or addressable from the public internet.” This makes them invisible to bad actors or unauthorized users, he said.
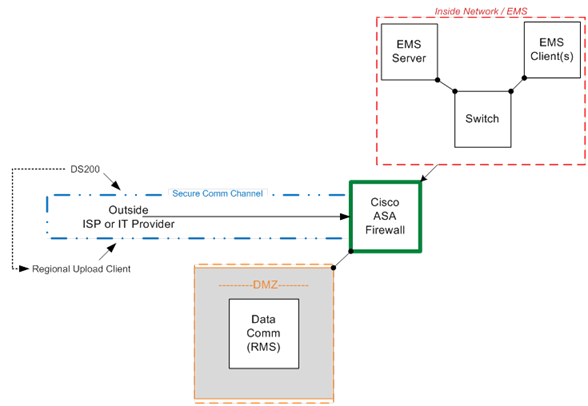
But Skoglund said this “misrepresents the facts.” Anyone who finds the firewall online also finds the election-management system connected to it.
“It is not air-gapped. The EMS is connected to the internet but is behind a firewall,” Skoglund said. “The firewall configuration [that determines what can go in and out of the firewall]… is the only thing that segments the EMS from the internet.”
And misconfigured firewalls are one of the most common ways hackers penetrate supposedly protected systems. The recent massive hack of sensitive Capital One customer data is a prime example of a breach enabled by a poorly configured firewall.
“If they did everything correctly [with the ES&S systems] as they say they do, there is no danger,” Robert Graham, CEO of Errata Security, told Motherboard. “These are all secure technologies that if [configured] correctly work just fine. It’s just that we have no faith that they are done correctly. And the fact that [election officials are] saying they aren’t on the internet and yet they are on the internet shows us that we have every reason to distrust them.”
Even proper configurations won’t secure a firewall if the firewall software itself has security vulnerabilities that allow intruders to bypass all the authentication checks, whitelisting rules, and other security parameters set in the firewall’s configuration file.
“If this system hasn’t been patched and has a critical vulnerability… you may be able to subvert any kind of security scheme that you’ve put in place,” Skoglund told Motherboard.
“Not only should ballot tallying systems not be connected to the internet, they shouldn’t be anywhere near the internet.”
While no one is suggesting that any of these systems have been manipulated or hacked, the findings highlight how little local and federal election officials understand how these critical election systems are really configured and connected, and the extent to which they are beholden to what the vendors tell them.
Senator Ron Wyden (D-Oregon) said the findings are “yet another damning indictment of the profiteering election vendors, who care more about the bottom line than protecting our democracy.” It’s also an indictment, he said, “of the notion that important cybersecurity decisions should be left entirely to county election offices, many of whom do not employ a single cybersecurity specialist.”
“Not only should ballot tallying systems not be connected to the internet, they shouldn’t be anywhere near the internet,” he added.%20speaks%20at%20a%20press%20conference%20alongside%20Speaker%20of%20the%20House%20Nancy%20Pelosi.jpg)
RON WYDEN (D-OR) SPEAKS AT A PRESS CONFERENCE ALONGSIDE SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE NANCY PELOSI (D-CA) ON PASSING THE AMERICA'S ELECTIONS ACT ON JUNE 26, 2019 IN WASHINGTON, DC. THE SAFE ACT BILL INCLUDES REFORMS TO SAFEGUARD VOTING SYSTEMS AND MODERNIZE ELECTION INFRASTRUCTURE IN AN EFFORT TO LOWER THE LIKELIHOOD OF HACKING. IMAGE: TASOS KATOPODIS/GETTY IMAGES
Wyden said two pieces of federal election security legislation that have stalled on Capitol Hill due to Republican leaders—the SAFE Act and a Wyden bill called PAVE Act—would effectively ban transmission of votes via modem and prohibit connecting any election-reporting or election-management system to the internet or to a telecommunications network at any time.
The ES&S firewalls are configured to only allow authenticated systems to connect and pass data through the firewall to the SFTP server; they also block outbound connections to the internet from systems behind the firewall. Authenticated systems include modem-enabled voting machines at voting precincts, or a computer at regional transmission sites. But even these authenticated systems, armed with passwords to communicate with the SFTP server, can only communicate with that server and cannot reach past this to the critical backend systems, according to ES&S. The passwords for the voting machines to communicate with the SFTP server are generated by the election-management system and passed to the voting machines on a USB flash drive when the systems are programmed before each election, and the passwords are also stored on the SFTP server to authenticate the machines.
The two backend systems—the reporting system that tabulates votes and the election-management system—sit on a local area network, which is connected to the Cisco firewall through a switch. The switch doesn’t provide additional security; it simply acts as a traffic cop to direct incoming data to the right system. To collect the encrypted votes the voting machines have deposited on the SFTP server, the backend reporting system reaches through the firewall to query the server every few minutes. If new files have arrived, the reporting system grabs those, decrypts them to read the votes inside, then tabulates them.
At least this is how the configuration in the diagram ES&S provided Motherboard works. But a different diagram the company submitted last year to Travis County, Texas, as part of a contract proposal, and which is available online, shows the reporting system and election-management system directly connected to the SFTP server through the switch, and all of them are connected to the firewall. This would mean the backend reporting system could bypass the firewall to reach the SFTP server directly, a less secure configuration. Weber of ES&S told Motherboard the Travis diagram is incorrect.
The backend systems in the ES&S configuration are only protected if the firewall rules ES&S has set up for controlling traffic are configured correctly, if the firewalls have no unpatched software vulnerabilities that would let an intruder bypass those protections to install malware on the SFTP server and the critical backend systems, and if the firewalls are also consistently maintained and monitored for rogue connections.
Unfortunately, there are a number of reasons to be concerned about the security of the firewalls and SFTP servers.
ES&S installs and configures the firewalls for the “majority” of its customers, the company told Motherboard. Counties then take over the maintenance or contract it out to a third party, which may even be ES&S in some cases.
Last year, the Cisco firewalls in Wisconsin failed to receive a patch for a critical vulnerability until six months after the vulnerability had been made public and the patch was released, Motherboard has learned. Patch delays aren’t unusual in states that require their election systems to be state certified as well as federally certified—a patch that needs to be applied to a certified system generally has to be reviewed for compliance with the certification requirements before it can be applied. But six months is a long time, and this means the systems were vulnerable to attack during a lengthy period before the 2018 midterm elections.
Another maintenance issue involves slow software upgrades. The researchers on Skoglund’s team discovered that seven of the SFTP servers on the ES&S systems they found are using outdated Cerberus FTP Server 6.0 software that the software maker stopped supporting in January 2017. This means that for the last two and a half years, the maker of that software has not updated it, and going forward will not produce patches if any vulnerabilities in the software are found. The current version is 10.0, and despite the fact that it has been available since November 2018, none of the ES&S SFTP servers the researchers found online are running it.
Not every ES&S backend election system is connected to the internet, because not every county opts to transmit election results. There are more than 33,000 ES&S DS200 optical scan machines with modems in use across eleven states and the District of Columbia. But ES&S told Motherboard it doesn’t know how many of its customers currently transmit results.
What’s not generally known by the public about ES&S election systems is that the company’s entire configuration for transmitting election results—from the modem to the SFTP server—is not certified by the Election Assistance Commission (EAC), which oversees the testing and certification of voting equipment at the federal level. ES&S voting machines are tested and certified, but the transmission configuration isn’t. The labs test them for functionality to make sure they transmit votes, and that’s it. In marketing literature, ES&S highlights the certified parts of its election system in blue and labels them "EAC Certified Configuration." The uncertified part is highlighted in white and labeled "Extended Configuration."
Weber told Motherboard that instead of federal certification, his company has focused on working with officials in states that allow modem transmission to test and certify the configuration under their own state certification programs. He said this includes a security assessment of the configuration. Asked which states do these security assessments, he cited Wisconsin, Florida, and Minnesota. But someone familiar with Wisconsin’s certification testing, who spoke on condition of anonymity, told Motherboard it doesn’t include a security assessment of the modem transmissions and configuration.
Hunting Election Systems
The researchers began looking for connected systems in July of 2018 after seeing repeated comments from state and local election officials as well as federal officials with the Election Assistance Commission, that voting machines and backend election systems are never connected to the internet.
Although these officials acknowledge that many voting machines use modems to transmit election results over cellular networks and landline connections, they have long insisted that modem transmissions don’t involve the internet. A New York Times story I wrote last year, however, showed that the modem transmissions do pass through the internet, and even an ES&S document that the company supplied to Rhode Island in 2015 calls the modem transmission of votes an “internet” transmission. A document for modem transmissions from voting machines made by Dominion Voting Systems—another top voting machine company in the country—similarly discusses TCP-IP and SSL, both protocols used for internet traffic.
AN ES&S DOCUMENT SUPPLIED TO RHODE ISLAND AND DATED 2015, WHICH CLEARLY SHOWS THE MODEM TRANSMISSION OF VOTES FROM THE COMPANY'S DS200 OPTICAL SCAN VOTING MACHINES GOING OVER THE INTERNET.
“The configurations show TCP-IP configuration and ‘SSL Optional,’ making it clear that at least the vendors know their systems are connecting through the internet, even if their election official customers do not realize it or continue to insist to the public that the systems are not connected to the internet,” Skoglund said.
Knowing the vote transmissions are going over the internet, the researchers decided to see if they could find the backend internet-connected systems that receive the transmitted votes. They discovered a method of searching for connected ES&S systems after one of their group stumbled across the IP address for an ES&S firewall in Rhode Island in a publicly available document.
After combing through other documents for ES&S systems published online, and finding technical specifications that show the systems use Cisco ASA 5500 series firewalls, and Cerberus FTP software and Cisco AnyConnect VPN for the vote transmissions, they used a specialized search engine called Censys to find connected systems that matched this configuration combination. Censys scans the internet weekly for connected devices and catalogues information about them, including their IP address, in a database. Their search led them to 35 connected systems over the last year, though Skoglund notes that there may actually be more ES&S systems connected to the internet that are not visible to Censys scans, since administrators can configure their connected devices to block automated scans. This doesn’t mean, however, that someone can’t still find the systems online.
When examining the ownership records for the IP addresses of the connected systems, at least four of them were registered to county governments in Michigan and Florida. This helped bolster the researchers’ belief that what they had found were county election systems. The other IP addresses were harder to trace, however, since they were registered to large internet service providers, and not the ISP customers using them.
The researchers found one or two systems online in Illinois, Indiana, Minnesota, Nebraska, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Iowa. The Nebraska system, they surmise, is probably a demo or test system for ES&S, which has its headquarters in Omaha. They also found two systems in Canada, where ES&S has field offices and customers, that may also be demo or test systems.
Although only one system was found online in Rhode Island, this one was particularly problematic, the researchers note. Rhode Island, unlike other states, conducts its elections from a centralized office at the state Board of Elections, instead of farming out election administration to each county or jurisdiction. The election reporting system the researchers found online, therefore, was the reporting system for the entire state.
One of the most dense states for online election systems was Florida, where the researchers found a number of connected systems that they believe belong to Bradford, Charlotte, Flagler, Wakulla, Miami-Dade, and Pasco counties, and one other county they’re unable to identity from the IP address.
Florida is known for its knuckle-biting elections. Trump won the state by just 1.2 percentage points in 2016, and in 2018 the state had senate and gubernatorial races that were too close to call on election night. Miami-Dade county in particular, with 1.4 million registered voters, is one of the most intensely watched counties in federal elections—it was using ES&S machines with embedded modems in the 2016 elections.
None of this implies that the election systems in Miami-Dade or any other Florida county were manipulated in the 2016 elections. But the findings highlight what is at stake with critical election systems online.
Any election system connected to the internet creates potential vulnerabilities for elections. But the nine systems in Wisconsin and four in Michigan that the researchers found raise particular red flags since these were two states among three where Green Party presidential nominee Jill Stein sought a recount of the 2016 presidential votes. All three states, which included Pennsylvania, produced results that were contrary to election polls and prior state voting trends. Although there was no specific evidence suggesting the election systems had been manipulated, a recount could have helped provide assurance to the public that this wasn’t the case. A court, however, halted the Michigan recount after it began, and a Pennsylvania court declined to hear Stein’s case for a recount in that state.
"What you are describing is a bad behavior amplified by sloppiness and complete negligence of security."
Wisconsin’s recount was completed, but some counties that used optical scan machines didn’t do a true recount—they simply ran the paper ballots through the optical-scan machines a second time, instead of manually comparing them against the digital tallies to uncover discrepancies. If any problems existed in the scanner software to produce incorrect results during the first scan, they would reproduce the same incorrect results in the re-scan.
The researchers repeated their searches of the Censys database periodically to see when systems dropped out of visibility or new ones popped up online. This allowed them to see the systems connected for long periods of time, contrary to assertions by election officials that the systems for transmitting results only remain connected for a few minutes after elections. Some of the systems do pop up online only around election times, but they tend to remain online about a month before disappearing, not a few minutes.
“Rhode Island is one that kind of comes on and goes off,” Skoglund said. “They don’t stay on year round. But others do.”
Motherboard asked Errata Security CEO Graham, who created an internet-scanning tool called Masscan, to independently verify the methodology the researchers used to find the systems, and he confirmed that the method was sound, using the search parameters the researchers provided. Like the researchers, though, he was unable to explore further without breaking the law, so he could only see the firewalls and not what is behind them. An independent election security expert named Harri Hursti, who consults with election districts and helps run the annual Voting Machine Hacking Village at the Def Con security conference, also verified the methodology for Motherboard without being told how to find the systems. Hursti in fact told Motherboard that many other election systems are online that the researchers’ particular search parameters missed.
The researchers didn’t single out ES&S election systems for their hunt. They also attempted to search for connected systems for the other top two voting machine vendors in the country—Dominion Voting Systems and Hart InterCivic. But Skoglund said the configuration footprints for these systems are less distinctive than ES&S’s footprint, resulting in the team finding thousands of systems that were clearly not election infrastructure.
Although the researchers have not been able to confirm with elections officials in every state that all of the firewalls they spotted are connected to ES&S systems, they were able to verify enough of them that Skoglund says he feels confident their list is reliable. And all of the systems the researchers found share a configuration footprint that, as far as they can tell, is unique to ES&S systems. Furthermore, the IP addresses for the firewalls of the non-confirmed systems all appear to be in counties that also use ES&S voting machines, according to a crosscheck against a web tool operated by Verified Voting, a nonprofit that tracks voting machine use around the country. Although resolving IP addresses to precise geographical location is difficult to do, the researchers were able to pinpoint the addresses they found to a specific city or region in all cases except four of the systems.
ES&S did not dispute that the firewalls the researchers found are ES&S systems; the company said it had no way of knowing one way or the other. Motherboard offered to provide the company with the IP addresses the researchers found for the firewalls, but the company said in an email that it doesn’t store customer IP addresses and therefore wouldn’t be able to tell if the systems belong to its clients.
Because the researchers only began looking for the systems last year, it’s not known how long they’ve been online, but it’s likely that some have been connected to the internet for years, going back to whenever a county first began to use modems to transmit election results.
ES&S has been selling systems with modems to transmit results for more than a decade. Wisconsin approved the use of its current ES&S DS200 optical scan voting machines, with modem transmission capability, in September 2015, but its previous generation of ES&S optical scan machines also used modems for transmitting results. It’s not clear if they used the same firewall and backend configuration.
Although election security experts oppose electronically transmitting votes at all, if a county is going to do it, the equipment set up to receive the results should not be connected to the internet when the system is not being used. It serves no other purpose than to receive results.
“While the [reporting systems] are secure, ES&S recommends that they only be connected to the internet when they are being tested or in use in order to minimize possible threats,” a statement sent to Motherboard from ES&S and the Wisconsin Election Commission says.
But Hursti told Motherboard it makes little difference how long election systems are connected; any connectivity at all opens them to potential attacks.
“For a skillful, motivated attacker, it doesn’t matter much if [the system is connected] two minutes or a whole year. But for a less skilled fool, less motivated attacker, the fact that they are there for a year, it lowers the bar,” he told Motherboard. “It actually buries the bar under the ground to carry out attacks with less skill. [And] you have a way longer time when the hack can be carried out and the evidence of the attacks [hidden]. What you are describing is a bad behavior amplified by sloppiness and complete negligence of security.”
A more skilled and motivated hacker—such as a Russia-backed nation-state hacker—could potentially compromise the firewall or SFTP server and plant malware that gets delivered to each voting machine that communicates with the server, Skoglund and Hursti said. This is similar to what security professionals refer to as a “watering hole” attack, named after predatory animals who lie in wait at watering holes for prey to arrive to drink.
And if hackers could push malware to the voting machines from the SFTP server, the malware could potentially reconfigure the modem on those machines to make them dial out to a system the attackers own, while preventing any evidence of these calls from showing up on the system’s log. This would give attackers time to subvert the machines for subsequent elections.
Findings Reported and Confirmed
The researchers reported the firewall IP addresses in August 2018 to the national Elections Infrastructure Information Sharing and Analysis Center (EI-ISAC)—a 24-hour watch center funded by the Department of Homeland Security and operated by the Center for Internet Security, a nonprofit established to develop and promote best practices in cybersecurity. The EI-ISAC provides election officials with security threat information and warnings, and told the researchers they would pass the information to where it needed to go, but the researchers never got any follow-up from the EI-ISAC.
A spokesperson for the group would not tell Motherboard if the information was disseminated to the affected counties, but the researchers did see some county systems disappear from the internet. The Department of Homeland Security, which has been working with states and counties since 2016 to secure their election infrastructures, also declined to speak with Motherboard about the researchers’ findings.
The fact that half of the systems were still online last week, however, highlights how new efforts by the federal government and information-sharing groups to warn election officials about known threats and vulnerabilities don’t work if the message doesn’t get to the people who can actually take the systems offline or if local election officials simply don’t act on the information they receive. Last year the researchers gave four IP addresses to the EI-ISAC that the researchers confirmed were connected to election infrastructure in Michigan and Florida.
“The two in Florida were taken offline in the following week or two,” Skoglund said. But the systems in two Michigan counties, Kalamazoo and Roscommon, were still online this week. A third Michigan system is also online, though the researchers are unable to pinpoint the county in which the IP address is located.
Similarly, they reported half a dozen IP addresses to Tony Bridges, election security lead at the Wisconsin Election Commission, for connected systems in Outagamie, Dodge, Milwaukee, St. Croix, Columbia, and Waukesha counties. But despite initial friendly communication, Skoglund said they never received a response.
Bridges told Motherboard he did act on the information he received, advising all of the counties to disconnect their systems when not in use for elections. He was surprised to learn last week from Motherboard that there were still systems online. He contacted the counties again, and Skoglund’s group could see that all off them dropped off except Milwaukee County’s system and another county they had not reported to Bridges last year, Eau Claire County.
The director of elections in Milwaukee County told Skoglund this week that their system was online for a special election next week. Skoglund told Motherboard that when he told her the system had actually been online since September 2018, she said she only learned last week that the systems should not be connected to the internet between elections.
Skoglund has also witnessed another problems as systems dropped offline after his group’s disclosure to a county; some IT workers are simply turning off the SFTP server or switching it to standby mode so traffic can’t come into it. But as long as the firewall is online, the backend systems are still connected to the internet and can be found. And if the AnyConnect VPN is still enabled, this also provides a potential pathway into those backend systems.
Skoglund said he’s concerned that no one is monitoring all of these systems once they’re online, and that counties are trusting the configuration instructions ES&S gives them, or trusting ES&S to configure the systems securely for them, and are then ignoring the systems once they’re set up.
“When a corporation sets up a firewall and a VPN … there is someone who is applying patches and monitoring logs … and really actively ensuring the security of the device to make sure it doesn’t become a vulnerability,” Skoglund said. “That’s a real question with election infrastructure. Who manages this hardware after it’s deployed? And what oversight is there?”
__
eof













